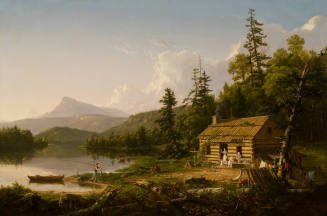Skip to main content
Cole actually painted two sets. The first, commissioned by banker and philanthropist Samuel Ward, Sr., the father of Julia Ward Howe, and completed in 1840, is in the collection of the Munson-Williams-Proctor Museum in Utica, New York. The second, 1841–1842, is in the collection of the National Gallery in Washington. In 1848, the American Art-Union, a subscription society that distributed paintings and prints to its members, purchased the Ward series and offered it as the prize in its annual lottery. In December of that year, subscriber J. Taylor Brodt won the four paintings. At the same time, the Art-Union commissioned James Smillie to make an engraving of Youth. [1] Smillie, a native of Edinburgh, Scotland, was already an accomplished engraver when he settled in New York in 1828. He was made a full member of the National Academy of Design in 1852, and worked closely with the Art-Union to reproduce the paintings the organization distributed to its membership.
In 1849, the Reverend Gorham D. Abbott purchased Brodt’s series and installed it in the Spingler Institute, a school for girls in New York City. That year, the Bulletin of the American Art-Union printed the following notice:
The [Spingler] Institute is an establishment of the highest class, for the education of young ladies, and these pictures are to be among the permanent decorations of its walls. It is with great satisfaction that we chronicle this act of wise liberality and enlightened taste. No where could there be found a more appropriate location than this for these works, which united so much purity of sentiment with so much artistic merit. We hope that other institutions of education will see the importance of calling into their service the ministrations of the Fine Art, to assist in informing the minds, and elevating the affections of their pupils, as well as to refine their tastes. [2]
In 1853, Abbott commissioned Smillie to produce a complete set of engravings of all four paintings, each bearing the words “From the original Painting by Thomas Cole in the possession of Rev. Gorham D. Abbott, Spingler Institute, New York.” The engravings were completed between 1853 and 1856, and a poetic inscription accompanied each one. [3]
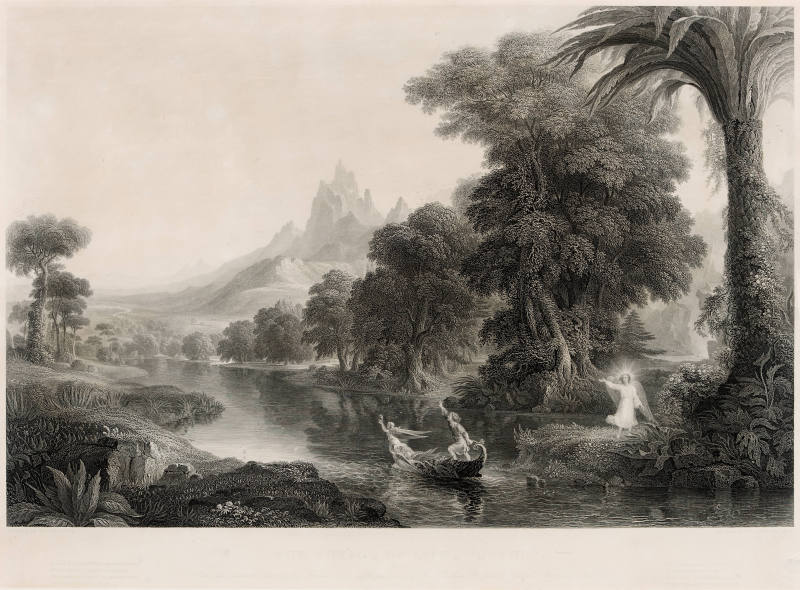
In Youth, childhood has given way to adolescence. The youth has left his angel-protector on the shore, seemingly forgotten, as he reaches for a shimmering mirage of a castle in the sky. His left hand grasps the rudder, suggesting that he is in charge of his own destiny now. The sun is higher in the sky, and the trees are in the full leaf of summer.
The engraved version of Youth bears this inscription:
Beware what earth calls happiness. Beware
All joys but joys that never can expire.
Who builds on less than an immortal base
Condemns his joys to death.
The golden palace of my God
Towering above the clouds I see:
Beyond the cherubs bright abode.
Higher than angels thoughts can be.
The production of the engravings enabled wide distribution of the images throughout the country. The series thus became an iconic and beloved allegory of man’s troubled, but ultimately redemptive, earthly experience.
Notes:
[1] Paul D. Schweizer, director of the Munson-Williams-Proctor Museum includes these details in his chronology of the production of The Voyage of Life, http://www.tfaoi.com/aa/2aa/2aa612e.htm
[2] Bulletin of the American Art Union. New York, 1849.
[3] Schweizer, http://www.tfaoi.com/aa/2aa/2aa612e.htm
ProvenanceTo 1983
Barbara B. Millhouse, New York, NY and Winston-Salem, NC [1]
From 1983
Reynolda House Museum of American Art, Winston-Salem, NC, given by Barbara B. Millhouse on December 29, 1983. [2]
Notes:
[1] Deed of Gift, object file.
[2] See note 1.
Exhibition History2010
Thomas Cole's Voyage of Life Series: Prints from the Reynolda Collection
Reynolda House Museum of American Art, Winston-Salem, NC (9/11/2010–2/20/2010)
2017
Samuel F.B. Morse's Gallery of the Louvre and the Art of Invention
Reynolda House Museum of American Art (02/17/2017 - 06/04/2017)
2021
The Voyage of Life: Art, Allegory, and Community Response
Reynolda House Museum of American Art (7/16/2021 - 12/12/2021)
Published References
DepartmentAmerican Art
Voyage of Life: Youth
Artist(after)
Thomas Cole
(1801 - 1848)
Date1853-1856
Mediumengraving
DimensionsFrame: 26 1/8 x 32 1/8 in. (66.4 x 81.6 cm)
Paper: 20 x 26 in. (50.8 x 66 cm)
Image (with text): 17 1/4 x 23 1/4 in. (43.8 x 59.1 cm)
SignedT. Cole 1840
Credit LineGift of Barbara B. Millhouse
CopyrightPublic domain
Object number1983.2.39.b
DescriptionIn Thomas Cole’s four-part The Voyage of Life, 1840, a river voyage symbolizes man’s journey through the stages of life. The series begins with an image of a child in a small boat guided by an angelic figure, then follows the character through youth, manhood, and old age as he attempts to navigate life’s treacherous waters.Cole actually painted two sets. The first, commissioned by banker and philanthropist Samuel Ward, Sr., the father of Julia Ward Howe, and completed in 1840, is in the collection of the Munson-Williams-Proctor Museum in Utica, New York. The second, 1841–1842, is in the collection of the National Gallery in Washington. In 1848, the American Art-Union, a subscription society that distributed paintings and prints to its members, purchased the Ward series and offered it as the prize in its annual lottery. In December of that year, subscriber J. Taylor Brodt won the four paintings. At the same time, the Art-Union commissioned James Smillie to make an engraving of Youth. [1] Smillie, a native of Edinburgh, Scotland, was already an accomplished engraver when he settled in New York in 1828. He was made a full member of the National Academy of Design in 1852, and worked closely with the Art-Union to reproduce the paintings the organization distributed to its membership.
In 1849, the Reverend Gorham D. Abbott purchased Brodt’s series and installed it in the Spingler Institute, a school for girls in New York City. That year, the Bulletin of the American Art-Union printed the following notice:
The [Spingler] Institute is an establishment of the highest class, for the education of young ladies, and these pictures are to be among the permanent decorations of its walls. It is with great satisfaction that we chronicle this act of wise liberality and enlightened taste. No where could there be found a more appropriate location than this for these works, which united so much purity of sentiment with so much artistic merit. We hope that other institutions of education will see the importance of calling into their service the ministrations of the Fine Art, to assist in informing the minds, and elevating the affections of their pupils, as well as to refine their tastes. [2]
In 1853, Abbott commissioned Smillie to produce a complete set of engravings of all four paintings, each bearing the words “From the original Painting by Thomas Cole in the possession of Rev. Gorham D. Abbott, Spingler Institute, New York.” The engravings were completed between 1853 and 1856, and a poetic inscription accompanied each one. [3]
In Youth, childhood has given way to adolescence. The youth has left his angel-protector on the shore, seemingly forgotten, as he reaches for a shimmering mirage of a castle in the sky. His left hand grasps the rudder, suggesting that he is in charge of his own destiny now. The sun is higher in the sky, and the trees are in the full leaf of summer.
The engraved version of Youth bears this inscription:
Beware what earth calls happiness. Beware
All joys but joys that never can expire.
Who builds on less than an immortal base
Condemns his joys to death.
The golden palace of my God
Towering above the clouds I see:
Beyond the cherubs bright abode.
Higher than angels thoughts can be.
The production of the engravings enabled wide distribution of the images throughout the country. The series thus became an iconic and beloved allegory of man’s troubled, but ultimately redemptive, earthly experience.
Notes:
[1] Paul D. Schweizer, director of the Munson-Williams-Proctor Museum includes these details in his chronology of the production of The Voyage of Life, http://www.tfaoi.com/aa/2aa/2aa612e.htm
[2] Bulletin of the American Art Union. New York, 1849.
[3] Schweizer, http://www.tfaoi.com/aa/2aa/2aa612e.htm
ProvenanceTo 1983
Barbara B. Millhouse, New York, NY and Winston-Salem, NC [1]
From 1983
Reynolda House Museum of American Art, Winston-Salem, NC, given by Barbara B. Millhouse on December 29, 1983. [2]
Notes:
[1] Deed of Gift, object file.
[2] See note 1.
Exhibition History2010
Thomas Cole's Voyage of Life Series: Prints from the Reynolda Collection
Reynolda House Museum of American Art, Winston-Salem, NC (9/11/2010–2/20/2010)
2017
Samuel F.B. Morse's Gallery of the Louvre and the Art of Invention
Reynolda House Museum of American Art (02/17/2017 - 06/04/2017)
2021
The Voyage of Life: Art, Allegory, and Community Response
Reynolda House Museum of American Art (7/16/2021 - 12/12/2021)
Published References
Status
Not on view